Where will design tech take you?
Digital School is Canada’s premier online technical design college for Architecture, Engineering and BIM. Our unique and personalized blended learning environment will teach you the practical skills and earn the credentials necessary for you to find your dream career.

FIND A PROGRAM THAT’S RIGHT FOR YOU
Digital School’s programs are designed for students who want a fast-paced, immersive learning experience with 24/7 flexibility. Learning online at Digital School is a seamless experience that values hands-on learning, real-time collaboration, and real-world projects by industry professional instructors.
ALL PROGRAMS ARE 100% ONLINE
Financial assistance may be available to those who qualify.
DIPLOMA PROGRAM
The architecture industry is constantly evolving as advancing technology and modern developments lead to new and exciting design and construction opportunities. Architectural Design Technology graduates play a vital role in the industry, working alongside architectural professionals to plan and execute sophisticated residential and commercial designs.
Full-time: 1 Year
Part-time: 2 Years
DIPLOMA PROGRAM
Engineering Design Technology
As an Engineering Design Technology graduate, you can enter a fulfilling, creative career and enjoy your future as an innovator, problem-solver, and visionary. You’ll help to design the products, machines, buildings, and transit systems that humans rely on, working directly with engineers and technologists to produce and analyze digital designs and to simulate and test machines, structures, and systems.
Full-time: 1 Year
Part-time: 2 Years
DIPLOMA PROGRAM
Engineering Design Technology with Process Piping Specialty
Engineering Design Technology students have the option of adding the Process Piping Specialty Certificate to their studies to gain specific preparation for careers in the production, analysis and testing of pressure vessels, storage tanks, process plant equipment and pipeline designs for chemical and food processing facilities, pharmaceutical, breweries, water treatment and petroleum industries.
Full-time: 1 Year
Part-time: 2 Years
CERTIFICATE PROGRAM
BIM Technician
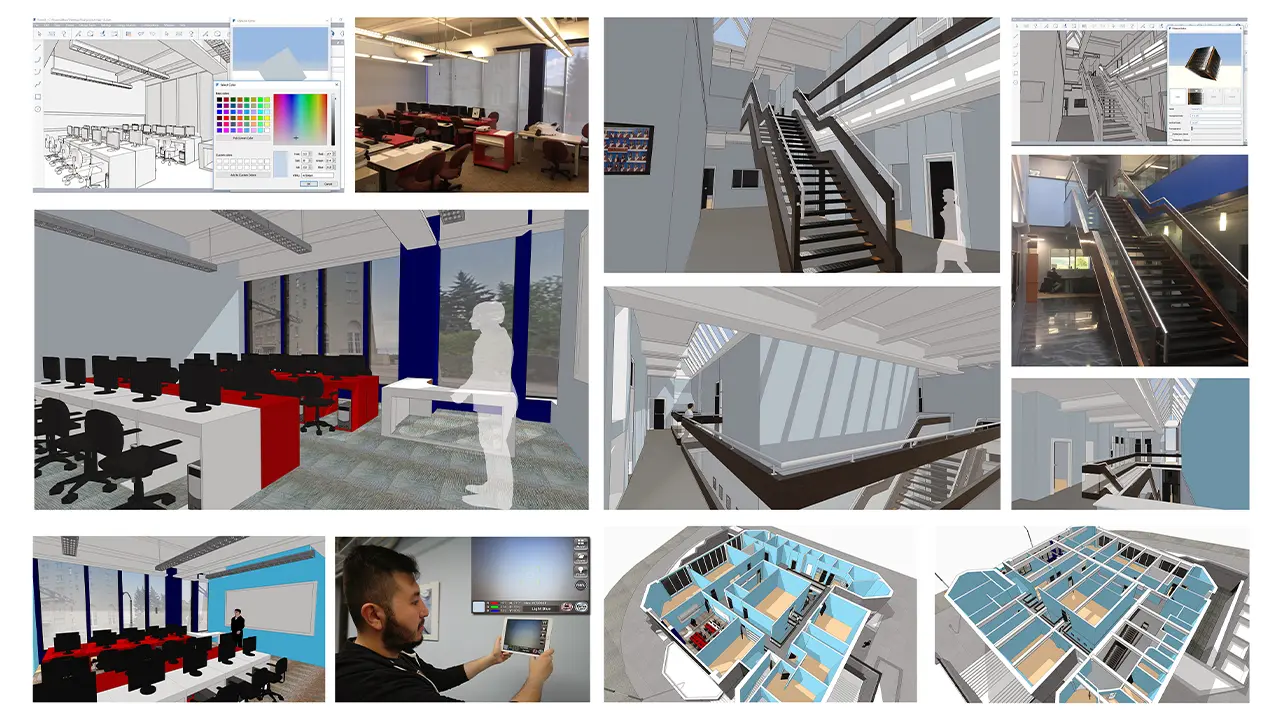
BIM Technicians work directly with designers, project managers, and engineers to translate a concept into technical drawings and BIMs that construction workers can build into a reality. Your career in design will support the entire building lifecycle including the concept / design, construction, and operations / maintenance phases.
Full-time: 6 Months
Part-time: 1 Year
TRAIN WITH PROFESSIONAL SOFTWARE
Digital School students get access to Autodesk design software, Office 365, creativity apps, and learning resources for FREE as part of their programs and for their devices. It’s the same software used every day by professional designers, engineers, architects, and more. This gives you the flexibility to create anywhere, at any time.
AutoCAD
Revit
Civil 3D
Inventor
FormIt
Digital School Technical Design College is an Autodesk Authorized Training Center

CAREER PATHS
Digital School students can choose a wide variety of career paths where companies rely on skilled technicians to help them produce and communicate design data in a range of work environments, including:
ARCHITECTURE
BIM / CAD MODELING
ENGINEERING
PROCESS PIPING
STRUCTURAL
MECHANICAL
MANUFACTURING
CONSTRUCTION
NEW EDUCATION FINANCING & SCHOLARSHIPS
Meet with us to learn about the new nation-wide financing and limited-time scholarship opportunities – no matter your situation, we’ll find the best financial support for you!
WHY DIGITAL SCHOOL?
START RIGHT AWAY
No need to wait. With our continuous, flexible intakes, students can begin when it works best for them!
GRADUATE FASTER
Our online programs are offered at an accelerated pace, which allows you to graduate faster than traditional colleges or universities.
INDUSTRY CERTIFICATION
Earn industry-recognized course completion certificates for Autodesk software skills, get Autodesk Certified when you take a certification exam and become eligible for Building Transformations Foundation Certification upon completion of BIM courses.
BIM TRAINING LEADER
Digital School is leading the way in ensuring our graduates are well-versed in Building Information Modeling (BIM), transitioning from computer-aided design (CAD) to BIM, and giving students the critical skills they need for the real world.
AUTODESK CERTIFIED
Our certified instructors have the Autodesk product knowledge and industry skills to meet the highest education standards and subject matter expertise in an instructional setting.
AWARD-WINNING LIBRARY
Digital School students receive a one-year subscription to the award-winning, GeT Everything library by Global eTraining! In addition to the required courses as part of your program, you can access training for any other Autodesk or AEC software you like.
CAREER SERVICES
The goal of Student Support Services is to help you meet your personal, academic, and career objectives and maximize your online college experience.
JOB PLACEMENT
Digital School offers assistance to current students and recent graduates with finding employment through recruitment and networking events, job boards, and our network of local employers.
Digital School Intro Video
WHAT OUR GRADUATES SAY
The experience of our students has always been the primary focus here at Digital School Technical Design College. That’s why we’re proud to share these inspiring success stories and testimonials from current students and alumni nationwide!
91% EMPLOYMENT RATE
We focus specifically on the skills, tools, and experience you need to find a successful career. On average, 91% of our graduates find employment within 3 months of graduating.
WHO HIRES OUR GRADS
Many of our graduates have gone on to great success in various firms, companies, and groups in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industries.
Looking to hire a graduate? Click the button below to get started.
JOIN AN ON-DEMAND WEBINAR
From the admissions interview process to our career placement program, and everything in between, we’ll give you the complete breakdown on how to earn more money, in a career you love with Digital School Technical Design College
LAUNCH YOUR CAREER IN DESIGN TECH TODAY!
You have questions. We have answers. Please fill out the form below, and we will respond shortly.
*By submitting this form, you agree to be contacted by Digital School Technical Design College through email and/or phone. You reserve the right to withdraw your consent at anytime.